Introduction
Have you ever wondered why some people seem to eat endlessly without gaining weight, while others gain pounds after a single indulgence? The answer often lies in metabolism—your body’s internal engine that burns calories for energy. If you’re in your 30s to 50s and looking to stay lean, energetic, and healthy, understanding how to boost your metabolism is a game-changer. In this guide, we’ll explore science-backed strategies, bust common myths, and share an easy-to-understand infographic to help you take action today.
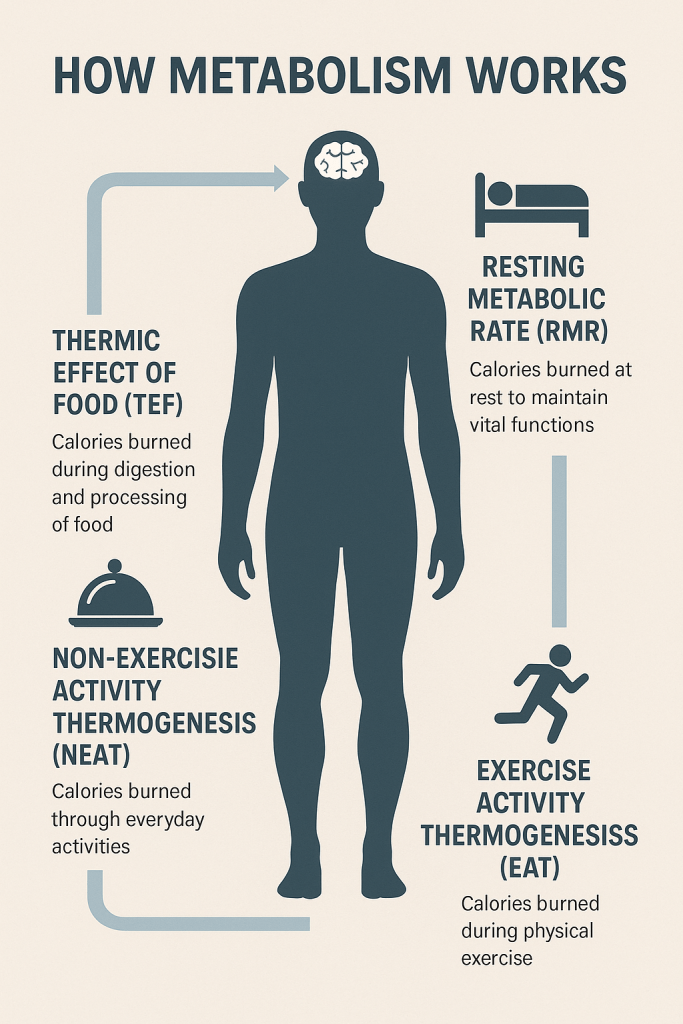
1. What Is Metabolism and Why It Slows Down
- Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in your body that convert food into energy.
- As we age, muscle mass naturally declines, leading to a slower resting metabolic rate (RMR).
- Sedentary lifestyles, poor diet, and hormonal changes also contribute to metabolic slowdown.
People Also Ask:
Q: What is resting metabolic rate?
A: Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) is the number of calories your body burns at rest to maintain essential functions like breathing, circulation, and cell repair. It accounts for about 60–75% of your total daily energy use.
Q: Does metabolism slow down after 30?
A: Yes, your metabolism starts to slow by about 1–2% per decade after age 30. This is primarily due to muscle loss, hormonal changes, and decreased physical activity.
Q: Is it normal to gain weight in your 40s?
A: Yes, many people gain weight in their 40s because of a slower metabolism, lifestyle factors, and reduced muscle mass. However, weight gain can be managed with the right habits.
2. Build Muscle to Burn More at Rest

- Strength training boosts your metabolism by increasing lean muscle mass.
- Muscle burns 3–5x more calories than fat, even when you’re not moving.
- Include resistance workouts 2–3 times a week—bodyweight, dumbbells, or machines all count.
People Also Ask:
Q: How does lifting weights increase metabolism?
A: Lifting weights builds lean muscle, which burns more calories than fat—even when you’re resting. This boosts your resting metabolic rate.
Q: What’s the best workout for fat burning?
A: A combination of strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) is most effective for fat burning and increasing metabolism.
Q: Can I gain muscle in my 40s?
A: Absolutely. With proper resistance training, protein intake, and recovery, people in their 40s (and even older) can gain muscle effectively.
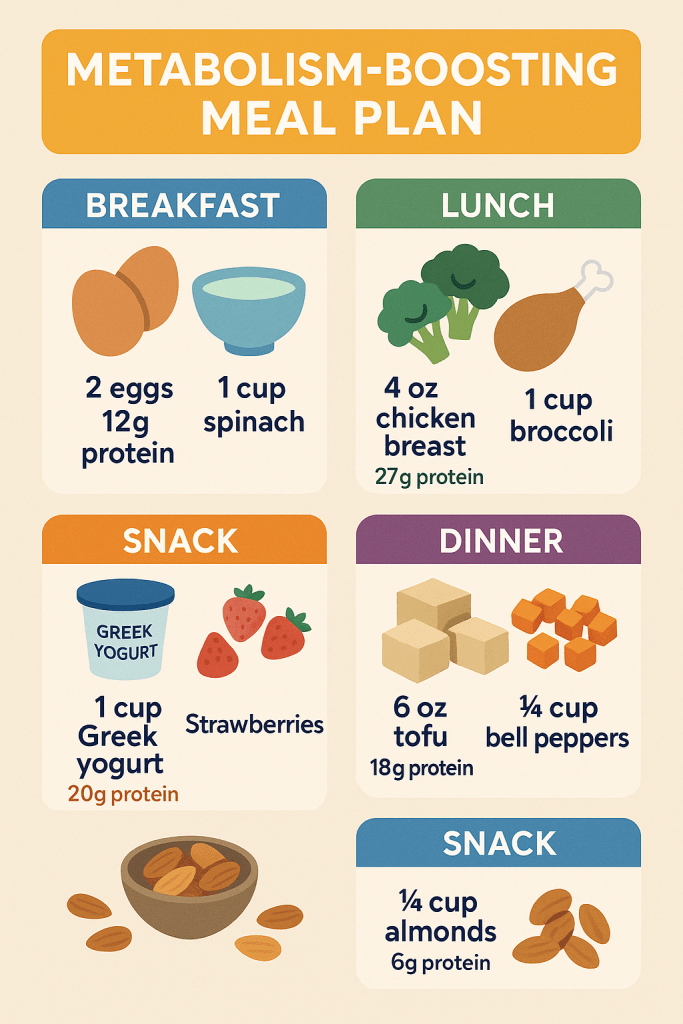
3. Eat Enough—Especially Protein
- Eating too little slows your metabolism as your body enters “starvation mode.”
- Protein-rich foods require more energy to digest (TEF = Thermic Effect of Food).
- Aim for 20–30g of protein per meal (e.g., eggs, tofu, chicken, Greek yogurt).
People Also Ask:
Q: Does protein really increase metabolism?
A: Yes. Protein has a high thermic effect of food (TEF), meaning your body burns more calories digesting it. This can boost metabolism temporarily.
Q: How many calories should I eat to boost metabolism?
A: It depends on your age, weight, and activity level, but under-eating can actually slow your metabolism. Use a calorie calculator to find your maintenance level and avoid dropping below that by more than 500 calories/day.
Q: Is starvation mode real?
A: “Starvation mode” refers to metabolic adaptation during extreme calorie restriction. While not a medical term, prolonged under-eating can cause your body to conserve energy and slow metabolism.
4. Move More Throughout the Day
- NEAT (Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis) includes everyday movement like walking, standing, fidgeting.
- You can burn an extra 300–500 calories daily just by being more active.
- Use a standing desk, take the stairs, walk while on calls.

People Also Ask:
Q: How many steps should I walk to boost metabolism?
A: Aim for at least 7,000–10,000 steps a day. Walking more increases NEAT (non-exercise activity thermogenesis), helping you burn extra calories consistently.
Q: Does sitting all day slow metabolism?
A: Yes, prolonged sitting reduces your daily energy expenditure and can negatively affect metabolic health over time.
Q: Is walking enough exercise?
A: Walking is a great start, especially when combined with strength training. It’s low-impact, boosts circulation, and burns calories.
5. Sleep and Stress: The Metabolism Killers
- Poor sleep messes with hormones like ghrelin and leptin, increasing appetite and fat storage.
- Chronic stress raises cortisol, which can lower metabolism and increase belly fat.
- Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep and reduce stress through meditation or hobbies.

People Also Ask:
Q: Can stress slow your metabolism?
A: Yes. Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, which can lead to fat storage, especially around the belly, and slow metabolism.
Q: Does sleeping more help you lose weight?
A: Quality sleep supports hormonal balance and appetite control, both of which are crucial for maintaining a healthy metabolism and body weight.
Q: Why do I crave sugar when I’m tired?
A: Sleep deprivation increases ghrelin (hunger hormone) and reduces leptin (satiety hormone), leading to stronger cravings—especially for sugar and carbs.
6. Try Safe Metabolism-Boosting Habits

- Drink cold water to temporarily boost calorie burn.
- Use spices like chili or ginger to raise body temperature slightly.
- Drink green tea or coffee (in moderation) for a natural stimulant effect.
- Avoid miracle pills or fad diets—stick with sustainable habits.
People Also Ask:
Q: Do cold showers increase metabolism?
A: They might offer a minor short-term boost by activating brown fat, which burns energy to generate heat, but the effects are modest.
Q: What drinks increase metabolism fast?
A: Green tea, black coffee, and cold water can slightly raise metabolism due to caffeine and thermogenic effects—but they’re not magic bullets.
Q: Are metabolism boosters safe?
A: Natural options like exercise, protein, and hydration are safe. Many over-the-counter “metabolism pills” are unregulated and can have side effects. Always check with a doctor before using supplements.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Metabolism
While you can’t control your age or genetics, you can control your habits. By staying active, eating enough protein, sleeping well, and reducing stress, you’ll naturally increase your metabolism and feel better daily. Ready to start? Try one new habit each week. Small changes, big results. 💪

Leave a comment